本文所分析的DDPM论文以及代码的相关信息如下:
一、 demo.py
首先由__init__初始化一些显示界面的参数,如进度条。
然后进入main()函数,在main()函数中完成了以下任务:
- 数据集、ema多选框、扩散步骤的预设置
get_state()实例化扩散过程,包括加载预训练的扩散模型、$x_T$、以及设定扩散步骤- 实时显示当前图像 $x_t$ 和 cur_step
- 根据页面触发的动作
Denoise和Diffuse来分别调用去噪函数和扩散函数,如下图: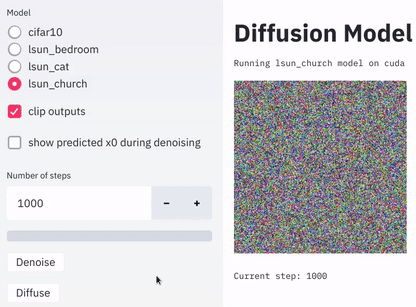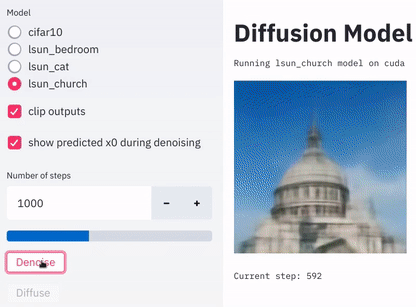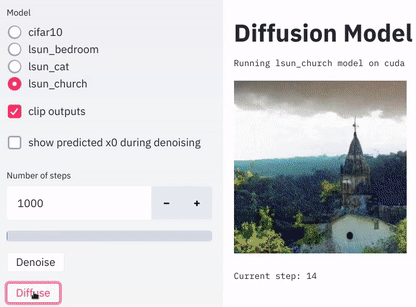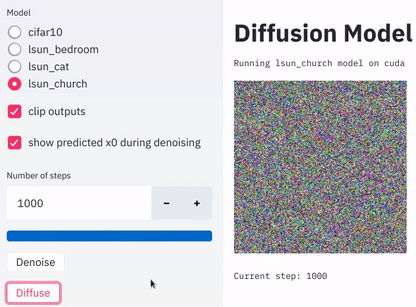
1def main():
2 #无关代码已省略 ......
3 name = st.sidebar.radio("Model", ("cifar10", "lsun_bedroom", "lsun_cat", "lsun_church"))
4 ema = st.sidebar.checkbox("ema", value=True)
5 state = get_state(name, ema=ema)
6 diffusion = state["diffusion"]
7 #"Number of steps" 默认为1000
8 n_steps = st.sidebar.number_input("Number of steps", min_value=1,max_value=diffusion.num_timesteps,value=diffusion.num_timesteps)
9 def callback(x, i, x0=None):
10 if show_x0 and x0 is not None:
11 x = x0
12 output.image(diffusion.torch2hwcuint8(x, clip=clip)[0])
13 step.text("Current step: {}".format(i))
14 callback(state["x"], state["curr_step"])#展示初始图像x_T和cur_step:1000
15
16 denoise = st.sidebar.button("Denoise")
17 if state["curr_step"] > 0 and denoise:#去噪
18 x = diffusion.denoise(1,
19 n_steps=n_steps, x=state["x"],
20 curr_step=state["curr_step"],
21 progress_bar=tqdm_factory,
22 callback=callback)#调用回调函数实时显示
23 state["x"] = x
24 state["curr_step"] = max(0, state["curr_step"]-n_steps)
25 diffuse = st.sidebar.button("Diffuse")
26 if state["curr_step"] < diffusion.num_timesteps and diffuse:#扩散
27 x = diffusion.diffuse(1,
28 n_steps=n_steps, x=state["x"],
29 curr_step=state["curr_step"],
30 progress_bar=tqdm_factory,
31 callback=callback)#调用回调函数实时显示
32 state["x"] = x
33 state["curr_step"] = min(diffusion.num_timesteps, state["curr_step"]+n_steps)
其中diffusion模型的实例化在get_state()函数中实现:
1def get_state(name, ema):
2 if ema:#判断是否使用滑动平均指数(ema)
3 name = "ema_"+name
4 diffusion = Diffusion.from_pretrained(name)#加载对应的预训练模型
5 state = {"x": diffusion.denoise(1, n_steps=0),
6 "curr_step": diffusion.num_timesteps,
7 "diffusion": diffusion}
8 return state
至此demo.py的功能基本介绍完毕,下面学习diffusion.py中的Diffusion类,查看具体扩散和去噪的实现。
二、Diffusion类
本文分析的代码是直接调用的预训练好的模型,因此没有训练过程。Diffusion类中实现的功能有:
- 类初始化,定义论文公式计算中需要的各参数
- 加载预训练模型的方法
- 去噪方法和扩散方法
- 保存生成的图片
其中定义的方法如下:
1class Diffusion(object):
2 #方法实现代码省略......
3 def __init__(self, diffusion_config, model_config, device=None):
4 def init_diffusion_parameters(self, **config):#初始化公式参数
5 def from_pretrained(cls, name, device=None):#加载预训练模型
6 def denoise(self, n, n_steps=None, x=None, curr_step=None,
7 progress_bar=lambda i, total=None: i,
8 callback=lambda x, i, x0=None: None):#去噪
9 def diffuse(self, n, n_steps=None, x=None, curr_step=None,
10 progress_bar=lambda i, total=None: i,
11 callback=lambda x, i: None):#扩散
12 def torch2hwcuint8(x, clip=False):#转化图像格式
13 def save(x, format_string, start_idx=0):#保存图像
1. init_diffusion_parameters()里面实现了论文公式中计算相关参数的定义,经过初始化后,可以得到相关属性:
- model_var_type —— 对应方差类别
- betas —— $\beta_t$ 相关的计算参数
- logvar —— 方差的对数

其中103行中调用get_beta_schedule()方法来决定 $\beta_{1:T}$ 序列的增长方式:
1def get_beta_schedule(beta_schedule, *, beta_start, beta_end, num_diffusion_timesteps):
2 if beta_schedule == 'quad':#二次方增长
3 betas = np.linspace(beta_start ** 0.5, beta_end ** 0.5, num_diffusion_timesteps, dtype=np.float64) ** 2
4 elif beta_schedule == 'linear':#线性增长
5 betas = np.linspace(beta_start, beta_end, num_diffusion_timesteps, dtype=np.float64)
6 elif beta_schedule == 'warmup10':#预热,训练初期较小,之后修改为预设的方式
7 betas = _warmup_beta(beta_start, beta_end, num_diffusion_timesteps, 0.1)
8 elif beta_schedule == 'warmup50':
9 betas = _warmup_beta(beta_start, beta_end, num_diffusion_timesteps, 0.5)
10 elif beta_schedule == 'const':#常数
11 betas = beta_end * np.ones(num_diffusion_timesteps, dtype=np.float64)
12 elif beta_schedule == 'jsd': # 1/T, 1/(T-1), 1/(T-2), ..., 1
13 betas = 1. / np.linspace(num_diffusion_timesteps, 1, num_diffusion_timesteps, dtype=np.float64)
14 else:
15 raise NotImplementedError(beta_schedule)
16 assert betas.shape == (num_diffusion_timesteps,)
17 return betas
2. from_pretrained()实现根据不同数据集加载对应预训练模型的功能,以cifar10为例:
1def from_pretrained(cls, name, device=None):
2 cifar10_cfg = { #模型的相关参数设置
3 "resolution": 32, #图像的分辨率
4 "in_channels": 3, #输入通道数
5 "out_ch": 3, #输出通道数
6 "ch": 128, #初始通道数
7 "ch_mult": (1,2,2,2), #通道数的倍数列表
8 "num_res_blocks": 2, #残差块数量
9 "attn_resolutions": (16,), #注意力机制的分辨率列表
10 "dropout": 0.1, #随机丢弃的比例
11 }
12 lsun_cfg = {... }
13 model_config_map = {"cifar10": cifar10_cfg,... }
14 diffusion_config = {
15 "beta_schedule": "linear",# β序列的获取方式为线性增长
16 "beta_start": 0.0001,
17 "beta_end": 0.02,
18 "num_diffusion_timesteps": 1000,#扩散步骤
19 }
20 model_var_type_map = { "cifar10": "fixedlarge",
21 "lsun_bedroom": "fixedsmall",...}#方差类别
22 ema = name.startswith("ema_")
23 basename = name[len("ema_"):] if ema else name
24 diffusion_config["model_var_type"] = model_var_type_map[basename]
25
26 print("Instantiating") #实例化中...
27 diffusion = cls(diffusion_config, model_config_map[basename], device)
28
29 ckpt = get_ckpt_path(name)#到对应的下载链接去下载模型
30 print("Loading checkpoint {}".format(ckpt))
31 diffusion.model.load_state_dict(torch.load(ckpt, map_location=diffusion.device)) # 加载模型
32 diffusion.model.to(diffusion.device)
33 diffusion.model.eval()
34 print("Moved model to {}".format(diffusion.device))
35 return diffusion
3. denoise()方法,循环 $T$ 步调用denoising_step()来完成去噪,并且实时显示去噪进度条。但是这里有一个比较疑惑的问题:callback这个回调函数的具体定义在main函数中, 用于实时显示当前图像$x_t$。
1def denoise(self, n, n_steps=None, x=None, curr_step=None,
2 progress_bar=lambda i, total=None: i,#lambda函数的用法
3 callback=lambda x, i, x0=None: None):
4 with torch.no_grad():
5 #省略无关代码......
6 if x is None: #初始将x_T设为来自高斯分布的随机噪声
7 x = torch.randn(n, self.model.in_channels, self.model.resolution, self.model.resolution)
8 x = x.to(self.device)
9 for i in progress_bar(reversed(range(curr_step-n_steps, curr_step)), total=n_steps):
10 t = (torch.ones(n)*i).to(self.device)
11 #调用denoising_step()进行从x_t到x_{t-1}的去噪
12 x,x0 = denoising_step(x,
13 t=t,
14 model=self.model,
15 logvar=self.logvar,
16 sqrt_recip_alphas_cumprod=self.sqrt_recip_alphas_cumprod,
17 sqrt_recipm1_alphas_cumprod=self.sqrt_recipm1_alphas_cumprod,
18 posterior_mean_coef1=self.posterior_mean_coef1,
19 posterior_mean_coef2=self.posterior_mean_coef2,
20 return_pred_xstart=True)
21 callback(x, i, x0=x0) #这个定义在main函数中
22 return x
4. diffuse()函数于上面的denoise()函数相似,在这里也是循环 $T$ 步,调用diffusion_step()函数进行前向扩散:
1 def diffuse(self, n, n_steps=None, x=None, curr_step=None,
2 progress_bar=lambda i, total=None: i,
3 callback=lambda x, i: None):
4 with torch.no_grad():
5 #省略无关代码......
6 for i in progress_bar(range(curr_step, curr_step+n_steps), total=n_steps):
7 t = (torch.ones(n)*i).to(self.device)#[i,i,...,i] i个i
8 x = diffusion_step(x, t=t,
9 sqrt_alphas=self.sqrt_alphas,
10 sqrt_one_minus_alphas=self.sqrt_one_minus_alphas)
11 callback(x, i+1) # 这个定义在main函数中
12 return x
三、核心函数
1. denoising_step()方法在denoise()第12行被调用,完成了 $p(x_{t-1}|x_t)$ 去噪采样过程,但并不是直接计算论文中的公式(11):
$$x_{t-1}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{\alpha_t}}(x_t-\frac{\beta_t}{\sqrt{1-\bar\alpha_t}}\epsilon_\theta(x_t,t))+\sigma_tz$$
而是通过以下步骤来获取同等效果:
- 首先,得到模型预测的噪声 $\epsilon_\theta(x_t,t)$
- 接着,由公式 $x_t=\sqrt{\bar\alpha_t}x_0+\sqrt{1-\bar\alpha_t}\epsilon$ , 计算得到预测的 $x_0 = \frac{1}{\sqrt{\bar{\alpha_t}}}x_t-\sqrt{\frac{1}{\bar\alpha_t}-1}\epsilon_\theta(x_t,t)$
- 计算 $q(x_{t-1} | x_t, x_0) = \mathcal{N}(x_{t-1},\tilde{\mu_t}(x_t,x_0),\tilde{\beta_t}I)$ 当中的均值和方差,
即 $\tilde{\mu_t}(x_t,x_0)=\frac{\sqrt{\bar\alpha_{t-1}}\beta_t}{1-\bar\alpha_t}x_0+\frac{\sqrt{\alpha_t}(1-\bar\alpha_{t-1})}{1-\bar\alpha_{t}}x_t$ - 利用重参数采样技巧,得到 $x_{t-1}=\tilde{\mu_t}(x_t,x_0)+\sigma_tz$ ,其中$\sigma_t=exp (\frac{1}{2}\log{\tilde{\beta_t}})=\sqrt{\tilde{\beta_t}}$
1def denoising_step(x, t, *,
2 model, #预测噪声的模型
3 logvar,#方差对数
4 sqrt_recip_alphas_cumprod,
5 sqrt_recipm1_alphas_cumprod,
6 posterior_mean_coef1,
7 posterior_mean_coef2,
8 return_pred_xstart=False):
9 # 1.得到模型预测的噪声ε_θ
10 model_output = model(x, t)
11 # 2.预测x_0
12 pred_xstart = (extract(sqrt_recip_alphas_cumprod, t, x.shape)*x -
13 extract(sqrt_recipm1_alphas_cumprod, t, x.shape)*model_output)
14 pred_xstart = torch.clamp(pred_xstart, -1, 1)#将输入张量各元素限制在[-1,1]
15 # 3. 计算均值与方差
16 mean = (extract(posterior_mean_coef1, t, x.shape)*pred_xstart +
17 extract(posterior_mean_coef2, t, x.shape)*x)
18 logvar = extract(logvar, t, x.shape)
19 # 4. 从高斯分布中采样z
20 noise = torch.randn_like(x)
21 mask = 1-(t==0).float() # t=0时,没有噪声
22 mask = mask.reshape((x.shape[0],)+(1,)*(len(x.shape)-1))
23 sample = mean + mask*torch.exp(0.5*logvar)*noise
24 sample = sample.float()
25 if return_pred_xstart:
26 return sample, pred_xstart
27 return sample
从第12行开始多次出现的extract()是用来提取系数的。
5. diffusion_step方法在diffuse()第8行被调用,完成了 $q(x_t | x_{t-1})$ 扩散采样过程,与去噪过程相比,简单得多:直接计算得到 $x_t=\sqrt{\alpha_t}x_{t-1}+\sqrt{1-\alpha_t}\epsilon_t$ .
1def diffusion_step(x, t, *,
2 noise=None,
3 sqrt_alphas,
4 sqrt_one_minus_alphas):
5 if noise is None: #从高斯分布中采样噪声ε
6 noise = torch.randn_like(x)
7 return (extract(sqrt_alphas, t, x.shape) * x +
8 extract(sqrt_one_minus_alphas, t, x.shape) * noise)